Trading Book
26 Feb 2020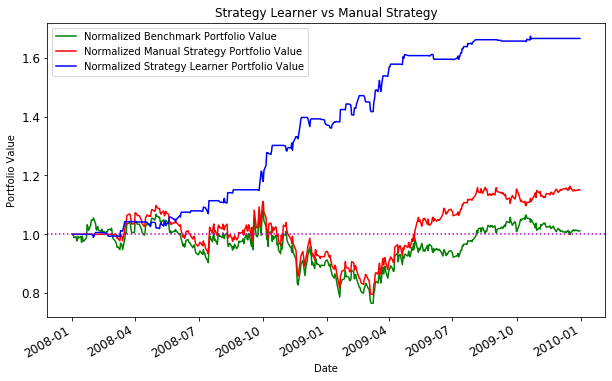
1.Background
I spent the last 2 days to build an algorithm trading starter notebook. It is essentially using a different approach compared to what we are doing now for the FX trading project. I would like to have this as an alternative starting point and compare the performance between 2 different approaches. To make it easier for others to compare, I took the data scientist poor engineering practice to commit data into a repo. The main techniques are learned from the course Machine Learning for Trading, taught by Tucker Balch, who left Georgia Tech to work for JP Morgan now.
1.1 AWS setup
I would like to recommend my favourite setup, by using AWS Deeplearning AMI (Google Cloud or Azure are mostly the same based on my experience). A normal p2.xlarge would be more than sufficient. If you prefer to work with Jupyter notebook, Fast.ai has awesome documentation about the setup.
1.2 Alternative setup
Another highly recommended tool is Google’s colab. I almost always use it for an experiment. The only thing is we need a bit of setup to use Google drive to insert data. This post showed how to connect Colab to Gdrive.
2.Method
Financial data are normally time series data. So sequential models like LSTM is a naturally a good choice, just like we used in our internal project. But in this notebook, we embedded time-series information into technical indicators, then for each day, apart from price, there are several technical indicators taking historical information as part of the input. In this way, we can use frameworks like Gradient boosted trees or Q-learning to train our dataset.
2.1 Assumption
We assume the Efficient Market Hypothesis is not holding, or at least semi-strong or strong form do not hold. But it should be a common-sense for quantitative trading hedge fund like Renaissance Technologies. There should be some signals or correlations in stock prices, but not for all. We need some methods to find them out.
2.2 Pipeline Demo
The processing pipeline is shown in the README.md.
The target of the model is 3 positions: HOLD, BUY and SELL. Each day we have price information about one stock, with selected technical indicators containing historical information. We trained the model to understand the position to take for each day, then based on the positions, we can find the holdings. Subsequently, we use daily holdings to calculate the orders we should make. Eventually, our final product is a order book of days we BUY or SELL particular stocks.
2.2.1 Backtesting
The starting point of backtesting is orders file. We should treat backtesting separately, and it is probably the most important thing of the whole pipeline. What we need to make sure is that the backtesting result and forward testing result are similar. This is a crucial point. But not in the discussion of this post. This notebook is served as a starting point of exploration.
3.Result
The experiment results without too much fine-tuning are shared in the notebook.
In the experiment, the ML model is performed much better, but I set the risk free rate to 0 and market impact to the minimum. There many more concerns about the market environment. So to make sure the model would perform well in the real market, we need to spend extra effort in fine-tuning backtesting model.
4.Future work
There are several things I would like to try out to make this notebook starter more robust.
- Use deep reinforcement learning approach.
- Use more mature frameworks like LightGBM, and process with more data.
- Try stacking and other ensembling methods.
- Integrate with news data.
- Apply to Two Sigma’s kaggle competition